Dr. Suresh, MBBS, MS, G.Surg, Mch CTVS
Cardiologist
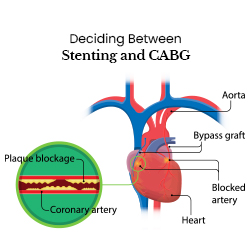
In today’s fast-paced world, where multi-factorial risks for heart attacks are becoming more prevalent, it’s crucial to understand the differences between two common treatment options: stenting and coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
In cases of acute myocardial infarction (AMI), rapid intervention is essential to prevent further damage. This blog explores the intricate aspects of AMI, the importance of assessing coronary complexity and clinical conditions, and the decision-making process for opting between stenting and CABG.
Understanding Acute Myocardial Infarction:
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, is a critical cardiovascular event with potentially life-threatening consequences. Rapid identification and intervention are imperative to minimize damage to the heart muscle. ECG (electrocardiogram) changes and echocardiogram findings are pivotal in diagnosing AMI. When a patient experiences an AMI, one of the primary considerations is whether to opt for stenting, CABG, or other interventions.
Opening Vessels: Angiogram, Stent, and Thrombolysis:
In the aftermath of an AMI, patients often undergo an angiogram to visualize the coronary arteries. This diagnostic procedure aids in determining the extent and location of the blockage. The decision to proceed with stenting or CABG depends on various factors, including the type and complexity of the coronary artery disease.
Stenting involves the placement of a stent, a small mesh-like tube, to open narrowed or blocked arteries. This procedure is generally straightforward, making it suitable for patients with a single-vessel occlusion or those in the early stages of coronary artery disease.
Thrombolysis, on the other hand, involves the administration of clot-busting medications to dissolve the blood clot causing the blockage. While effective in certain scenarios, it may not be the primary choice for everyone and must be carefully considered based on the patient’s condition and the time elapsed since the onset of symptoms.
Deciding Between Stenting and CABG:
The decision to choose between stenting and CABG is intricate and requires a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s condition. Two primary factors play a pivotal role in this decision-making process: the complexity of coronary disease and the patient’s clinical condition.
Complexity of Coronary Disease:
- Stenting is often preferred for patients with less complex coronary artery disease, especially those with single-vessel occlusion or non-complex double-vessel occlusion.
- Stenting is a relatively straightforward procedure, making it suitable for cases where the blockages are accessible and less challenging to address.
However,
- CABG is more complex and is often considered when dealing with left main coronary artery disease or complex multi-vessel disease.
- Patients with extensive blockages, especially in critical arteries, may benefit more from the surgical approach offered by CABG.
Clinical Condition:
- Stenting is generally preferred for patients in the advanced stages of frailty or those with multiple risk factors for surgery.
- It is a less invasive procedure, allowing for quicker recovery and reduced stress on the patient’s overall health.
However,
- CABG might be more beneficial for patients with left ventricular dysfunction or those who are diabetic.
- Under circumstances where the patient has an association with other cardiac problems, or if heart disease requires a more comprehensive intervention, CABG is often the preferred choice.
The Heart Team Approach:
The decision between stenting and CABG is not a one-size-fits-all scenario. It demands a collaborative effort from a diverse team of specialists. At Trilife, our Heart Team approach includes a cardiac surgeon, a cardiologist, an anesthetist, and other healthcare professionals such as rehabilitation specialists and physiotherapists.
At the forefront of this collaborative effort is the Heart Team’s responsibility to sit down with the patient and their family. Together, they discuss the risks and benefits of each procedure, aiming to provide the patient with comprehensive information to make an informed decision.
In the case of hospitals like Trilife, where a large cardiology department is involved, this collaborative approach ensures that every aspect of the patient’s health is taken into consideration. The team evaluates the individual’s risk factors, overall health condition, and the specific characteristics of their coronary artery disease.
Conclusion:
The decision between stenting and CABG in the treatment of coronary artery disease is a nuanced process that requires a careful assessment of the patient’s coronary complexity and clinical condition. Stenting is often the preferred choice for less complex cases, while CABG is considered for more intricate situations involving left main coronary artery disease or significant multi-vessel disease.
The Heart Team approach, involving specialists from various disciplines, ensures that the decision-making process is well-informed and patient-centered. By discussing the risks and benefits of each procedure with the patient and their family, the Heart Team plays a crucial role in guiding individuals towards the most appropriate treatment for their specific condition.
Ultimately, the goal is to provide personalized and effective care, recognizing that every patient is unique and may require a tailored approach to coronary artery disease treatment.