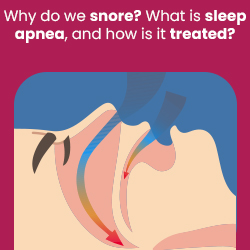
What Causes Snoring?
Snoring occurs when air flows through a narrowed airway during sleep. As throat muscles relax, the airway can constrict, causing vibrations that produce the sound of snoring. Some of the risk factors for OSA include
- Obesity: Excess weight can contribute to narrowed airways.
- Hypothyroidism: An underactive thyroid can lead to muscle weakness, affecting the airway.
- Diabetes: This condition can increase the risk of upper airway narrowing.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can contribute to sleep apnea.
Snoring vs. Obstructive Sleep Apnea
While snoring can be a nuisance, it doesn’t always indicate a major health problem. However, it can be a red flag for obstructive sleep apnea. In OSA, the airway becomes so narrow that breathing is repeatedly blocked or significantly reduced during sleep. This lack of oxygen triggers the brain to briefly wake you up, often without your conscious awareness. These disruptions fragment your sleep cycle, leaving you feeling tired and unrested in the morning.
Health Risks of Sleep Apnea
The constant struggle to breathe during sleep in OSA has serious consequences. During these episodes:
- Oxygen levels fall: The body is deprived of vital oxygen, impacting organ function.
- Brain wakes you up: Fragmented sleep leaves you feeling tired and disrupts sleep stages crucial for memory, concentration, and overall health.
- Heart under pressure: The heart works harder to pump blood despite low oxygen levels, increasing the risk of heart attack or stroke.
Common Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Here are some common signs of sleep apnea:
- Severe snoring: Loud, frequent snoring that disrupts sleep for you or your partner.
- Difficulty breathing at night: Snorting, gasping, or choking sensations during sleep.
- Daytime sleepiness: Excessive sleepiness during the day, even after a full night’s sleep.
- Early morning headaches: Frequent headaches upon waking.
- Non-refreshing sleep: Feeling tired and unrested despite sleeping for hours.
Diagnosing Sleep Apnea
If you suspect you or your partner might have sleep apnea, it’s important to get evaluated. Here’s how to determine the severity of the problem:
- Polysomnography (Sleep Study): This overnight test measures brain waves, heart rate, oxygen levels, breathing patterns, and muscle activity during sleep, providing a comprehensive picture of your sleep health.
- Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy (DISE): This test involves using medication to induce sleep while a flexible scope is inserted through the nose to examine the upper airway and identify areas of obstruction.
Effective Sleep Apnea Treatments
The good news is that sleep apnea is a treatable condition. Here are some treatment options depending on the severity of your case:
- Lifestyle Modifications : Maintaining a healthy weight, reducing alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking can all help improve airway function.
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP Therapy) : This device uses a mask to deliver a gentle stream of pressurized air to keep the airway open during sleep.
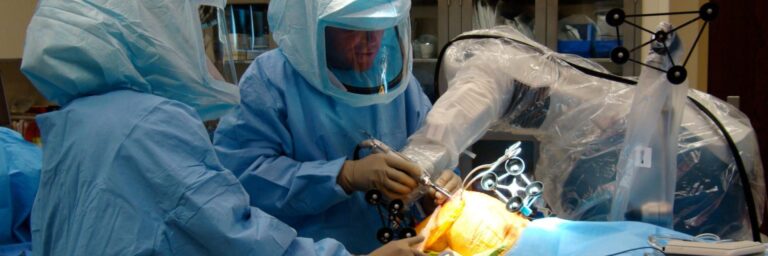
- Surgery : In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove or reshape tissues that obstruct the airway, such as uvulopalatoplasty (UPPP), which corrects the shape of the upper throat.
The Importance of Quality Sleep
Quality sleep is vital for physical health, mental clarity, and emotional balance. If snoring or sleep apnea affects your rest, seek medical advice. Prioritizing sleep health is key to a happier, healthier life.By optimizing lifestyle choices and exploring treatment options, you can restore restful sleep and improve overall well-being.
Dr. Sharath G. , Consultant ENT.